In the dynamic realm of agricultural economics, price controls in the Florida orange market present a captivating case study. This paper delves into the history, mechanisms, and multifaceted impacts of price controls, exploring their potential benefits and drawbacks while examining viable alternatives for managing orange prices.
Market Overview: Price Controls In The Florida Orange Market
The Florida orange market is a major industry in the state, with oranges being the largest citrus crop grown in Florida. The market is characterized by a high degree of seasonality, with the majority of oranges being harvested during the winter months.
In recent years, the market has been impacted by a number of factors, including weather conditions, disease outbreaks, and changes in consumer demand.
Orange prices in Florida have been relatively stable in recent years, with the average price per pound hovering around $0.25. However, prices have been subject to significant fluctuations, with prices rising sharply during periods of high demand and falling during periods of oversupply.
The market is also characterized by a high degree of concentration, with a small number of large growers controlling a significant share of the market.
Factors Influencing Orange Production
Orange production in Florida is influenced by a number of factors, including weather conditions, disease outbreaks, and changes in consumer demand. Weather conditions, such as hurricanes and freezes, can have a significant impact on orange production, as they can damage trees and reduce yields.
Disease outbreaks, such as citrus greening, can also have a negative impact on production, as they can weaken trees and reduce fruit quality.
Consumer demand for oranges is also a major factor influencing production. Changes in consumer preferences, such as a shift towards healthier eating habits, can lead to changes in demand for oranges. Additionally, changes in the global economy can also impact demand for oranges, as they can affect the price of oranges relative to other commodities.
Price Controls
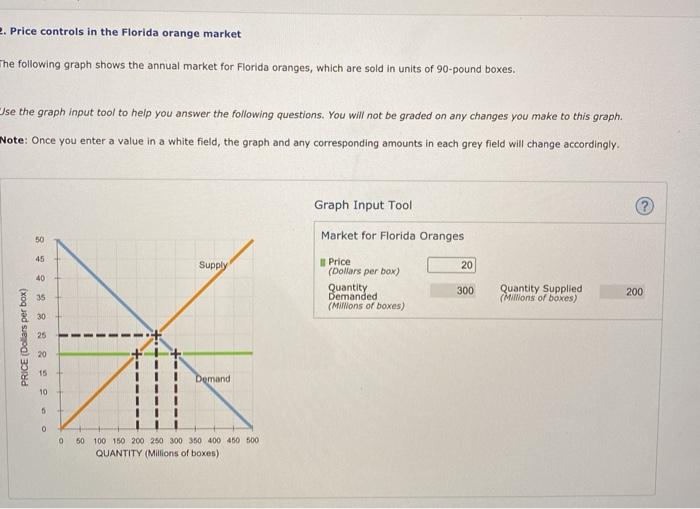
Price controls have been implemented in the Florida orange market at various times in history. The most recent instance of price controls was in the 1990s, when the Florida Citrus Commission implemented a price floor for oranges. The price floor was intended to stabilize prices and protect growers from low prices.
However, the price floor was ultimately unsuccessful, as it led to a surplus of oranges and a decline in prices.
Rationale Behind Price Controls
The rationale behind implementing price controls is to stabilize prices and protect producers from low prices. Price controls can also be used to ensure that consumers have access to affordable food. In the case of the Florida orange market, price controls have been used to protect growers from low prices caused by oversupply or disease outbreaks.
Specific Mechanisms Used to Implement Price Controls
There are a number of different mechanisms that can be used to implement price controls. These mechanisms include quotas, price ceilings, and price floors. Quotas limit the quantity of a good that can be produced or sold. Price ceilings set a maximum price that can be charged for a good.
Price floors set a minimum price that can be charged for a good.
Impact of Price Controls
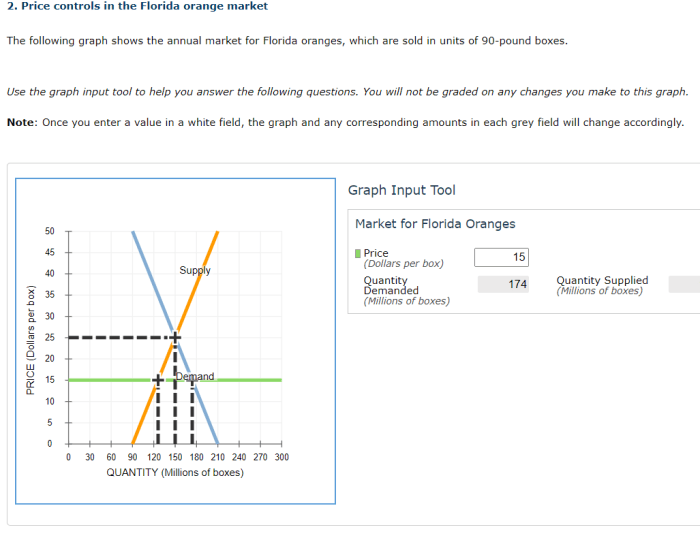
Price controls can have a significant impact on prices, supply, and demand. Price controls can stabilize prices, but they can also lead to shortages or surpluses. Price controls can also reduce incentives for production, as producers may be discouraged from producing a good if the price is set too low.
Potential Benefits of Price Controls
There are a number of potential benefits to price controls. Price controls can stabilize prices, which can benefit both producers and consumers. Price controls can also protect producers from low prices, which can help to ensure the long-term viability of the industry.
Potential Drawbacks of Price Controls
There are also a number of potential drawbacks to price controls. Price controls can lead to shortages or surpluses, as they can distort the market. Price controls can also reduce incentives for production, as producers may be discouraged from producing a good if the price is set too low.
Alternatives to Price Controls
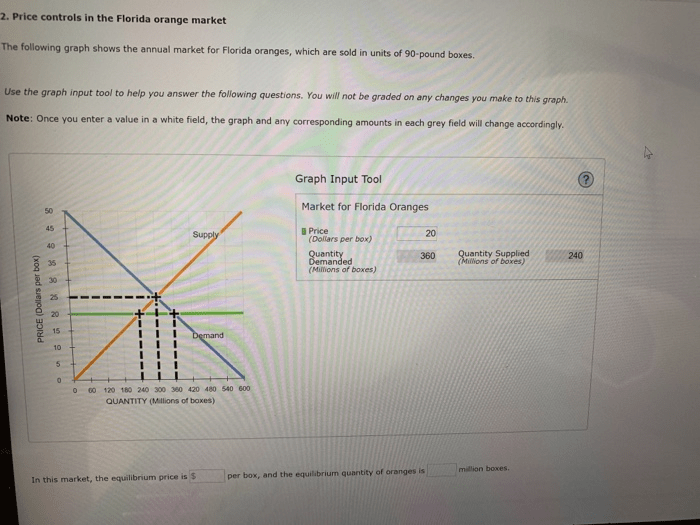
There are a number of alternative mechanisms for managing orange prices. These mechanisms include market-based solutions, such as futures contracts and options, and government subsidies. Market-based solutions allow producers to manage their price risk, while government subsidies can help to offset the costs of production.
Market-Based Solutions
Market-based solutions, such as futures contracts and options, allow producers to manage their price risk. Futures contracts are agreements to buy or sell a good at a set price at a future date. Options give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a good at a set price at a future date.
These contracts can help producers to lock in a price for their product, which can reduce their risk of loss.
Government Subsidies, Price controls in the florida orange market
Government subsidies can help to offset the costs of production for orange growers. These subsidies can take a variety of forms, such as direct payments to growers or tax breaks. Government subsidies can help to make orange production more profitable, which can lead to increased production and lower prices for consumers.
General Inquiries
What are the primary objectives of price controls in the Florida orange market?
Price controls aim to stabilize orange prices, protect consumers from price fluctuations, and ensure a fair return for orange growers.
How do price controls impact the supply and demand of oranges?
Price controls can lead to surpluses or shortages, depending on whether prices are set above or below equilibrium levels.
What are some potential drawbacks of price controls?
Price controls can distort market signals, reduce incentives for production, and lead to inefficiencies in resource allocation.