Welcome to the definitive resource for understanding moderate sedation post test answers. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of moderate sedation, providing a thorough examination of its indications, pharmacology, monitoring, and post-procedural care. Whether you’re a healthcare professional seeking to enhance your knowledge or a patient seeking to make informed decisions, this guide will empower you with the essential information you need.
As we navigate the complexities of moderate sedation, we’ll explore the different levels of sedation, discuss the risks and benefits, and examine the factors that determine the need for moderate sedation. We’ll also delve into the pharmacology of moderate sedation agents, providing a detailed analysis of their mechanism of action, onset time, duration of action, and side effects.
This knowledge will equip you with a solid foundation for selecting and dosing moderate sedation agents.
Understanding Moderate Sedation
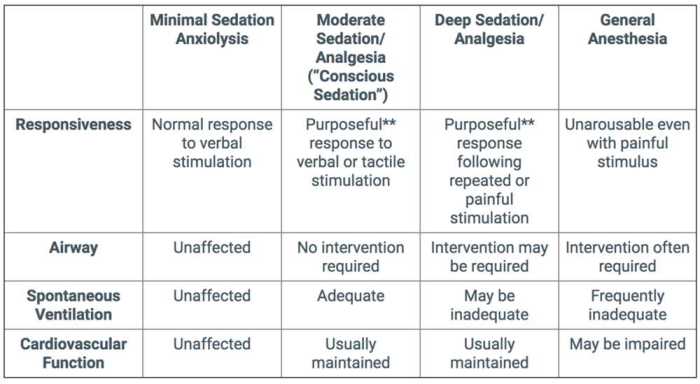
Moderate sedation, also known as conscious sedation, is a state of depressed consciousness in which the patient responds purposefully to verbal or tactile stimulation and maintains spontaneous ventilation.
The primary purpose of moderate sedation is to alleviate anxiety, reduce discomfort, and provide amnesia during medical procedures. It is typically used in situations where local anesthesia is not sufficient to control pain or anxiety.
Levels of Moderate Sedation, Moderate sedation post test answers
- Minimal sedation:The patient is relaxed, alert, and oriented but may experience some drowsiness.
- Moderate sedation:The patient is drowsy but can be easily aroused with verbal or tactile stimulation.
- Deep sedation:The patient is difficult to arouse but responds purposefully to repeated or painful stimulation.
Risks and Benefits of Moderate Sedation
Risks
- Respiratory depression
- Hypotension
- Nausea and vomiting
- Allergic reactions
Benefits
- Reduced anxiety and discomfort
- Improved patient cooperation
- Amnesia during the procedure
Indications for Moderate Sedation
Moderate sedation is commonly used for various medical procedures, including:
- Endoscopy
- Bronchoscopy
- Colonoscopy
- Dental procedures
- Painful dressing changes
- Reduction of fractures
The need for moderate sedation is determined by several factors, including:
- Patient’s age and health status
- Procedure complexity and duration
- Patient’s anxiety level
Before moderate sedation, a thorough patient assessment is essential to identify potential risks and determine the appropriate level of sedation.
Pharmacology of Moderate Sedation Agents
| Agent | Mechanism of Action | Onset Time | Duration of Action | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Midazolam | Benzodiazepine | 2-5 minutes | 30-60 minutes | Respiratory depression, hypotension, nausea, vomiting |
| Propofol | GABAA agonist | 15-30 seconds | 5-10 minutes | Respiratory depression, hypotension, pain on injection |
| Fentanyl | Opioid | 1-2 minutes | 30-60 minutes | Respiratory depression, nausea, vomiting, constipation |
| Ketamine | NMDA receptor antagonist | 30-60 seconds | 20-30 minutes | Psychedelic effects, hallucinations, increased salivation |
The selection and dosing of moderate sedation agents depend on the patient’s individual needs and the specific procedure being performed.
Monitoring and Management During Moderate Sedation
During moderate sedation, the patient’s vital signs, including oxygen saturation, respiratory rate, heart rate, and blood pressure, must be closely monitored.
The healthcare team should be trained in the management of moderate sedation and be prepared to intervene if necessary. This includes administering supplemental oxygen, administering reversal agents, and managing airway emergencies.
The criteria for terminating moderate sedation include:
- The procedure is complete.
- The patient is fully awake and alert.
- The patient’s vital signs are stable.
Post-Procedural Care After Moderate Sedation
After moderate sedation, the patient should be monitored in a recovery area until they are fully awake and their vital signs are stable.
Potential complications after moderate sedation include:
- Respiratory depression
- Hypotension
- Nausea and vomiting
- Allergic reactions
Patient education and discharge planning are essential to ensure a safe recovery.
Essential Questionnaire: Moderate Sedation Post Test Answers
What is moderate sedation?
Moderate sedation is a state of depressed consciousness in which the patient responds purposefully to verbal commands, either alone or accompanied by light tactile stimulation. It is typically used to provide anxiolysis, analgesia, or both during medical procedures.
What are the risks of moderate sedation?
The risks of moderate sedation include respiratory depression, hypotension, and airway obstruction. These risks can be minimized by careful patient selection, appropriate monitoring, and proper sedation techniques.
What are the benefits of moderate sedation?
The benefits of moderate sedation include reduced anxiety, improved pain control, and enhanced patient comfort during medical procedures.