Embark on an illuminating journey into the realm of autosomal pedigrees, where the intricacies of genetic inheritance unfold before our eyes. Delving into the autosomal pedigrees worksheet answer key, we uncover a treasure trove of knowledge that empowers us to decipher the patterns of genetic inheritance, predict disease risk, and provide invaluable guidance in genetic counseling.
Autosomal pedigrees, meticulously crafted diagrams that trace the transmission of genetic traits through generations, serve as indispensable tools for unraveling the complexities of human inheritance. By scrutinizing these pedigrees, we gain insights into the modes of inheritance, identify carriers and affected individuals, and assess the risk of genetic disorders within families.
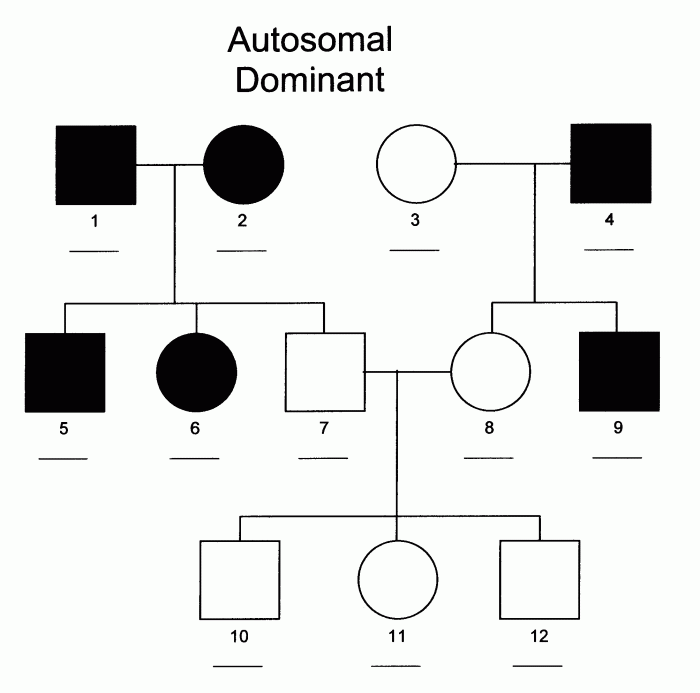
Autosomal Pedigrees
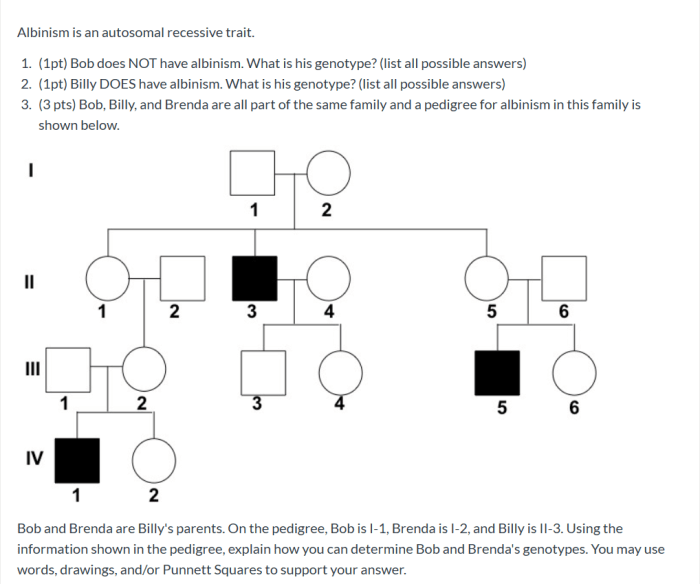
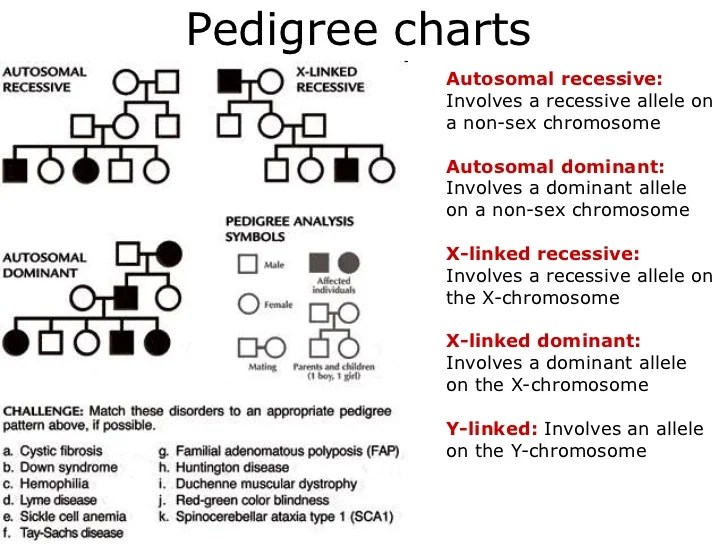
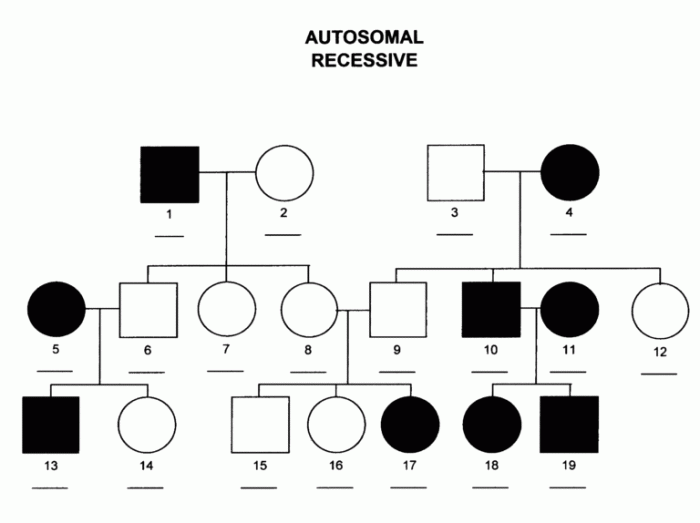
Autosomal pedigrees are family trees that chart the inheritance of traits that are located on autosomes, which are the non-sex chromosomes. They are used to trace the transmission of genetic disorders and to identify individuals at risk for developing these disorders.
Autosomal dominant pedigrees show a pattern of inheritance in which affected individuals have at least one copy of the mutant gene. Unaffected individuals have two copies of the normal gene. Dominant traits are expressed even when only one copy of the mutant gene is present.
Autosomal recessive pedigrees show a pattern of inheritance in which affected individuals have two copies of the mutant gene. Unaffected individuals have one copy of the mutant gene and one copy of the normal gene. Recessive traits are only expressed when both copies of the gene are mutant.
Inheritance Patterns
The inheritance patterns observed in autosomal pedigrees can be classified into three main categories: Mendelian, non-Mendelian, and mitochondrial.
- Mendelian inheritancefollows the laws of inheritance proposed by Gregor Mendel. These laws state that genes are inherited independently of each other and that each parent contributes one allele for each gene to their offspring.
- Non-Mendelian inheritancerefers to patterns of inheritance that do not follow the laws of Mendelian inheritance. These patterns can be caused by a variety of factors, such as gene linkage, pleiotropy, and epigenetic effects.
- Mitochondrial inheritancerefers to the inheritance of traits that are located on the mitochondrial DNA. Mitochondrial DNA is inherited only from the mother, so mitochondrial traits are passed down from mothers to their children.
Pedigree Analysis
Autosomal pedigrees can be analyzed to identify carriers, affected individuals, and at-risk individuals. Carriers are individuals who have one copy of the mutant gene but do not show any symptoms of the disorder. Affected individuals have two copies of the mutant gene and show symptoms of the disorder.
At-risk individuals have one copy of the mutant gene and are at risk for developing the disorder.
Pedigree analysis can also be used to determine the mode of inheritance of a particular disorder. The mode of inheritance can be determined by looking at the pattern of inheritance in the pedigree. For example, if a disorder is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, then affected individuals will have at least one affected parent.
If a disorder is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, then affected individuals will have two unaffected parents who are both carriers of the mutant gene.
Genetic Counseling, Autosomal pedigrees worksheet answer key
Genetic counseling is a process in which a trained healthcare professional provides information and support to individuals and families who are at risk for or affected by genetic disorders. Genetic counselors can use pedigrees to assess risk and to provide guidance on family planning and other reproductive options.
Genetic counseling can help individuals and families to make informed decisions about their health and reproductive choices. Genetic counselors can also provide support and guidance to individuals and families who are coping with the challenges of living with a genetic disorder.
Case Studies
Case studies can be used to illustrate the application of autosomal pedigree analysis. For example, a case study could be used to show how a pedigree can be used to diagnose a genetic disorder or to predict inheritance patterns.
Case studies can also be used to demonstrate the role of genetic counseling in interpreting autosomal pedigrees. For example, a case study could be used to show how a genetic counselor can use a pedigree to assess risk and to provide guidance on family planning and other reproductive options.
Questions and Answers: Autosomal Pedigrees Worksheet Answer Key
What are autosomal pedigrees?
Autosomal pedigrees are diagrams that trace the inheritance of traits carried on autosomes, the non-sex chromosomes.
What is the difference between autosomal dominant and recessive pedigrees?
In autosomal dominant pedigrees, the trait is expressed in individuals who inherit only one copy of the mutant allele. In autosomal recessive pedigrees, the trait is only expressed in individuals who inherit two copies of the mutant allele.
How can pedigrees be used to predict inheritance patterns?
By analyzing pedigrees, geneticists can identify patterns of inheritance and predict the likelihood of an individual inheriting a particular trait or disorder.