Embark on a captivating journey into the intricacies of cardiovascular anatomy with our comprehensive sheep heart dissection worksheet pdf. This invaluable resource empowers students, educators, and medical professionals alike to delve into the complexities of the sheep’s heart, providing a profound understanding of its structure, function, and clinical significance.
Through meticulous dissections and detailed explanations, this worksheet guides you step-by-step through the external and internal anatomy of the sheep’s heart, unraveling the intricate network of chambers, valves, and blood vessels that orchestrate the vital process of circulation.
1. Introduction
The sheep heart is a vital organ that plays a crucial role in the circulatory system. Its intricate structure and function are essential for maintaining the health and well-being of the animal. Dissection of the sheep heart provides a unique opportunity to explore its anatomy, understand its physiological processes, and gain insights into cardiovascular health.
2. Materials and Methods
Materials
- Sheep heart
- Dissection tray
- Scalpel
- Forceps
- Scissors
Steps
- Open the pericardial sac and remove the heart.
- Identify the chambers (right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle) and major blood vessels (aorta, pulmonary artery, superior and inferior vena cava).
- Cut open the chambers and examine the valves (tricuspid valve, pulmonary valve, mitral valve, aortic valve).
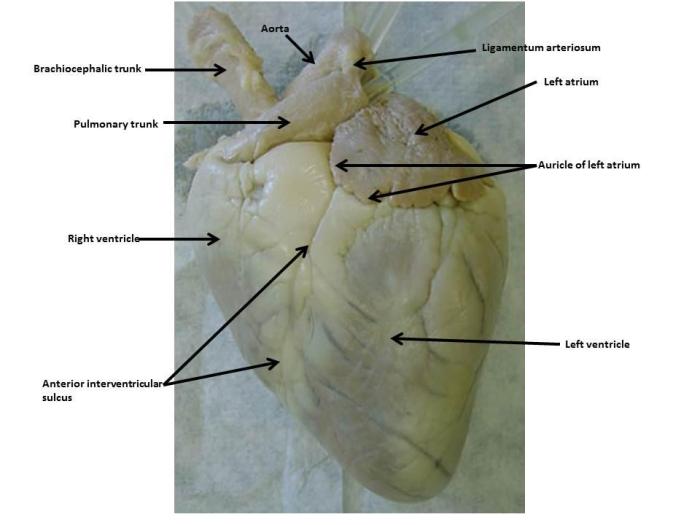
3. External Anatomy: Sheep Heart Dissection Worksheet Pdf
The sheep heart is a cone-shaped organ located in the thoracic cavity. It is enclosed in a protective sac called the pericardium, which prevents friction and provides lubrication.
4. Internal Anatomy

Chambers
- Right atrium:Receives deoxygenated blood from the body via the superior and inferior vena cava.
- Right ventricle:Pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs via the pulmonary artery.
- Left atrium:Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the pulmonary veins.
- Left ventricle:Pumps oxygenated blood to the body via the aorta.
Valves
- Tricuspid valve:Prevents backflow of blood from the right ventricle into the right atrium.
- Pulmonary valve:Prevents backflow of blood from the pulmonary artery into the right ventricle.
- Mitral valve:Prevents backflow of blood from the left ventricle into the left atrium.
- Aortic valve:Prevents backflow of blood from the aorta into the left ventricle.
Blood Flow
Blood flows through the heart in a specific pattern: right atrium → right ventricle → pulmonary artery → lungs → pulmonary veins → left atrium → left ventricle → aorta → body.
5. Physiology of the Heart
Electrical Conduction System
The electrical conduction system of the heart coordinates heart contractions. It consists of the sinoatrial node (SA node), atrioventricular node (AV node), bundle of His, and Purkinje fibers.
Cardiac Cycle, Sheep heart dissection worksheet pdf
The cardiac cycle consists of systole (contraction) and diastole (relaxation). During systole, the ventricles contract and pump blood out of the heart. During diastole, the ventricles relax and fill with blood.
6. Clinical Applications
Sheep heart dissection has clinical applications in understanding cardiovascular diseases and developing surgical techniques. It helps medical students visualize the heart’s anatomy and physiology, enabling them to diagnose and treat heart conditions in humans.
7. Educational Value
Sheep heart dissection provides an invaluable educational experience for students studying anatomy, physiology, and cardiovascular health. It allows them to explore the heart’s intricate structure, understand its function, and appreciate the complexity of living organisms.
User Queries
What is the purpose of dissecting a sheep’s heart?
Dissecting a sheep’s heart provides a hands-on opportunity to study the anatomy and function of the cardiovascular system, enabling a deeper understanding of its structure and physiological processes.
What materials are required for the dissection?
Essential materials include a sheep’s heart, dissection tray, scalpel, forceps, scissors, and dissection gloves.
What are the main structures identified during the dissection?
The dissection reveals the heart’s chambers (atria and ventricles), valves (tricuspid, pulmonary, mitral, and aortic), major blood vessels (aorta, pulmonary artery, and vena cava), and electrical conduction system.